Professor Yan Li:Lung-targeted polyzwitterionic lipid nanoparticles for effective treatment of lung diseases
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are non-viral nucleic acid delivery systems that show great potential in vaccine development and disease treatment. The recent approval of three LNP-based RNA drugs, including Patisiran, mRNA-1273, and BNT162b2, has triggered a great interest in this kind of safe and effective non-viral carrier. LNPs are typically composed of ionizable cationic lipids, amphipathic phospholipids, cholesterol and poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)-lipids. Although LNPs are particularly advantageous for in vivo delivery, the wide application of LNPs is impeded as their systemic delivery of nucleic acid drugs to extrahepatic tissues remains highly challenging.
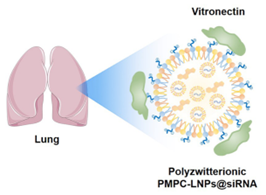
This work developed lung-targeted polyzwitterionic LNPs with zwitterionic polymer poly(2-methyacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) (PMPC) modified 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycerol lipid to replace the PEG-lipid for the delivery of small interfering RNA (siRNA). By regulating the degree of polymerization of the zwitterionic polymer and the proportion of each component of the LNPs, three libraries with 90 PMPC-LNPs@siRNA were established. The polyzwitterionic PMPC-LNPs had high siRNA encapsulation efficiency of about 90%. The findings revealed that polyzwitterionic PMPC-LNPs@siRNA absorbed protein corona with the main component of Vitronectin, mediating lung-targeted delivery of siRNA. With good cellular uptake and endo/lysosomal escape ability, in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that polyzwitterionic PMPC-LNPs with siRNA against tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) could significantly down-regulate the TNF-α in mRNA and protein levels, and improved the pathological features of lung inflammation. Polyzwitterionic PMPC-LNPs@siRNA achieved safe and efficient treatment of lung inflammation. Therefore, this work offered a promising siRNA therapeutic approach for lung diseases. This work has been published in Science China Chemistry (2025, 68, 1107-1116).
Link: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-024-2295-8


